ISO/IEC 27001:2022- Information security, cybersecurity and privacy protection — Information security management systems — Requirements.
Euro Veritas has already updated itself, with the requisite criteria, including updation of its Auditors to ISO 27001:2022. Euro Veritas is capable to issue new Certificates towards ISO 27001:2022 and / or transition certificates.

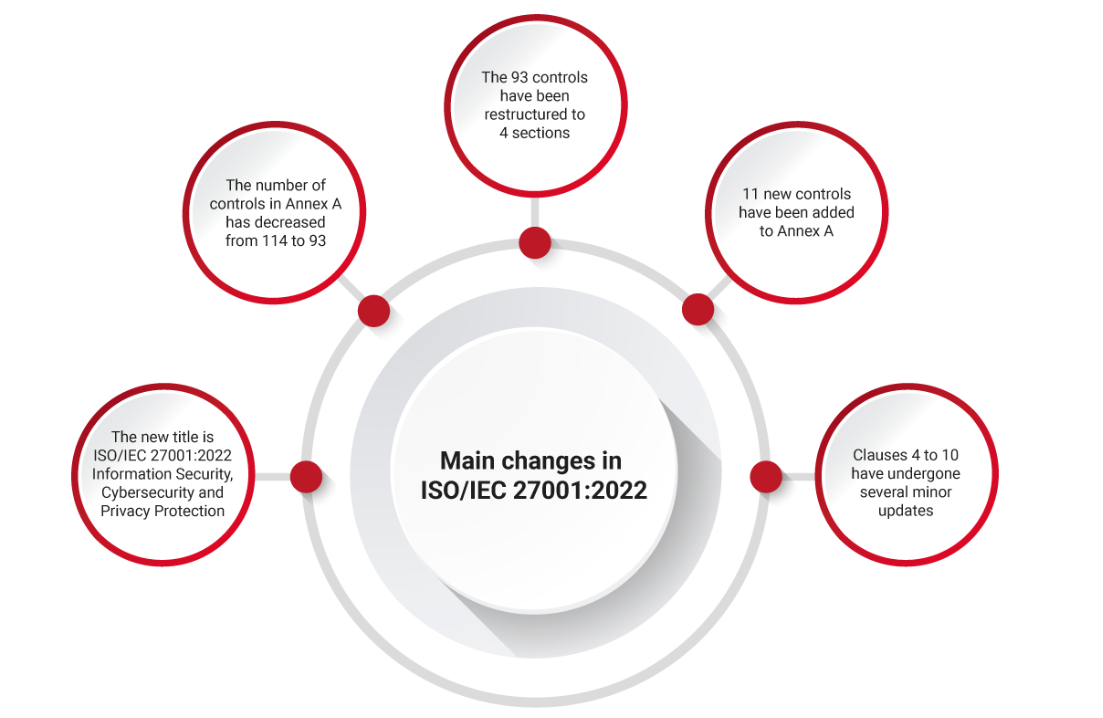
Different from ISO/IEC 27001:2013, the new version’s complete title is ISO/IEC 27001:2022 Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection. The part that has gone under the most significant changes is Annex A of ISO/IEC 27001 which is aligned with the ISO/IEC 27002:2022 updates, published earlier. As for other parts, clauses 4 to 10 have undergone several minor changes, especially in clauses 4.2, 6.2, 6.3, and 8.1 where additional new content has been added. Other updates include minor changes in the terminology and restructuring of sentences and clauses.
However, the title and order of these clauses remain the same:
Clause 4 Context of the organization
Clause 5 Leadership
Clause 6 Planning
Clause 7 Support
Clause 8 Operation
Clause 9 Performance evaluation
Clause 10 Improvement
What you need to know if your organization has an ISO 27001:2013 certification:
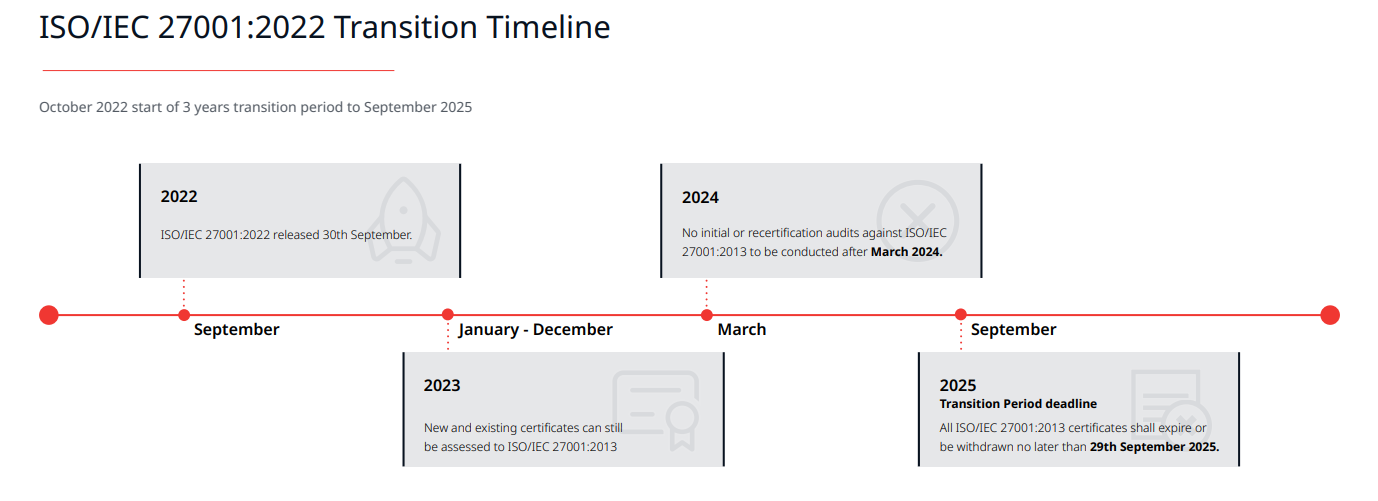
1. You will have until 31st October 2025 to update your existing ISMS and make the transition of the certification to ISO 27001:2022. After 31st October 2025 all ISO 27001:2013 certificates will be obsolete.2. Euro Veritas will need to conduct a transition assessment within this time period and issue you an updated certificate of ISO 27001:2022.
3. The transition assessment will determine whether you have updated your ISMS to the new requirements of ISO 27001:2022 including the changes to Annex A controls.
4. You can transition at any time, including during surveillance audits, a recertification audit or a stand alone assessment.
ISO/IEC 27001, Information Security Management and the ISO/IEC 27002, Controls for Information Security standards have been updated in 2022 to reflect the global digital evolution and new business practices becoming more cloud and digitally reliant. These 2 new standards will require you to implement changes to ensure you not only remain compliant but align your infosec requirements with the digitalization of business practices and the accompanying threats.
Major Changes to the ISO 27001 standard:
First, there are some editorial changes, including:
“International standard” replaced with “document” throughoutRe-arranging of some English phrases to allow for easier translation
Then, there are changes to align with the ISO harmonized Annex L approach:
Numbering re-structuring.
Requirement to define processes needed for implementing the ISMS and their interactions, including synchronisation with CIA model.
Explicit requirement to communicate organizational roles relevant to information security within in the organization.
New clause 6.3 – Planning of Changes.
New requirement to ensure the organization determines how to communicate as part of clause 7.4.
New requirements to establish criteria for operational processes and implementing control of the processes.
There are key changes in this revision- ISO 27001:2022 in Annex A, reflecting the changes made in ISO/IEC 27002:2022. These changes are:
The structure has been consolidated into 4 key areas:Organizational, People, Physical and Technological instead of 14 in the previous edition.
Controls listed have decreased from 114 to 93:
Some controls have been merged, some have been removed, new ones have been introduced, and others updated.
The concept of attributes has been introduced:
Aligned with common terminology used within digital security, these five attributes are: Control type, Information security properties, Cybersecurity concepts, Operational capabilities, and Security domains
The new control groups of ISO/IEC 27001:2022 are:
1. A.5 Organizational controls - contains 37 controls
2. A.6 People controls - contains 8 controls
3. A.7 Physical controls - contains 14 controls
4. A.8 Technological controls - contains 34 controls
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 has also added the below-mentioned 11 new controls to its Annex A:
1. Threat intelligence
2. Information security for the use of cloud services
3. ICT readiness for business continuity
4. Physical security monitoring
5. Configuration management
6. Information deletion
7. Data masking
8. Data leakage prevention
9. Monitoring activities
10. Web filtering
11. Secure coding
The controls now also have five types of ‘attribute’ to make them easier to categorise:
Control type (preventive, detective, corrective)
Information security properties (confidentiality, integrity, availability)
Cybersecurity concepts (identify, protect, detect, respond, recover)
Operational capabilities (governance, asset management, etc.)
Security domains (governance and ecosystem, protection, defence, resilience)
ISO 27001:2022 is not significantly different from ISO 27001:2013, but there are some notable changes:
Context and scope:You must now identify the “relevant” requirements of interested parties and determine which will be addressed through the ISMS (information security management system).
The ISMS now explicitly includes the “processes needed and their interactions”.
Planning:
Information security objectives must now be monitored and made “available as documented information”. There is a new section on planning changes to the ISMS. This does not specify any processes that must be included, so you should determine how you can demonstrate that changes to the ISMS have indeed been planned.
Support:
The requirements to define who will communicate and the processes for effecting communication have been replaced by a requirement to define “how to communicate”.
Operation:
The requirement to plan how to achieve information security objectives has been replaced by a requirement to establish criteria for processes to implement actions identified in Clause 6, and to control those processes in line with the criteria. Organisations are now required to control “externally provided processes, products or services” relevant to the ISMS rather than just processes.
Performance and evaluation:
Methods of monitoring, measuring, analysing and evaluating the effectiveness of the ISMS now need to be comparable and reproducible.
The management review must now also consider changes in the needs and expectations of interested parties.
Annex A:
Annex A has been revised to align it with ISO 27002:2022.



