Occupational health and safety management systems — Requirements with guidance for use
ISO 45001:2018 is an International Standard published from ISO, as the replacement for OHSAS 18001:2007- this standard specifies the basic requirements for an occupational health and safety (OH&S) management system, and gives guidance for its use, to enable organizations to provide safe and healthy workplaces by preventing work-related injury and ill health, as well as by proactively improving its OH&S performance.
ISO 45001:2018 is applicable to almost any organization that wishes to establish, implement and maintain an OH&S management system to improve occupational health and safety, eliminate hazards and minimize OH&S risks (including system deficiencies), take advantage of OH&S opportunities, and address OH&S management system nonconformities associated with its activities.
The International Standard ISO 45001:2018 certification from [Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK] helps the organization to achieve the intended outcomes of its OH&S management system. Consistent with the organization's OH&S policy, the intended outcomes of an OH&S management system include:
a) Hazard analysis and risk assessment;
b) continual improvement of OH&S performance;
c) fulfilment of legal requirements and other requirements;
d) achievement of OH&S objectives.
ISO 45001:2018 is applicable to any organization regardless of its size, type and activities. It is applicable to the OH&S risks under the organization's control, taking into account factors such as the context in which the organization operates and the needs and expectations of its workers/personnel and other interested parties.
ISO 45001:2018 is very generic in nature and does not state specific criteria for OH&S performance, nor is it prescriptive about the design of an OH&S management system.
ISO 45001:2018 enables an organization, through its OH&S management system, to integrate other aspects of health and safety, such as worker wellness/wellbeing.
ISO 45001:2018 does not address issues such as product/service safety, property damage or environmental impacts, beyond the risks to workers and other relevant interested parties.
ISO 45001:2018 can be used in whole or in part to systematically improve occupational health and safety management. However, claims of conformity to this document are not acceptable unless all its requirements are incorporated into an organization's OH&S management system and fulfilled without exclusion.
What is ISO 45001?
As per [Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK], to help protect employees/personnel and visitors from work-related incidents and accidents and health related diseases, the International Organization for Standardization developed the ISO 45001 standard, which represents the an international standard for occupational health and safety — OH&SMS.
Many workers, globally, lose their jobs and lives each day to preventable instances of adverse workplace conditions. As per the ISO and International Labour Organization — or ILO — as per official figures, the total number of workers who die every day from accidents and work-related diseases exceeds 7,600, which adds up to more than 2.7 million lives lost every year across the globe. There is a multiple times more fatalities, which actually are never reported due to the absurd nature of the organizations / companies.
ISO 45001 certification from [Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK] was being done through audits to mitigate any factors that can cause employees and businesses irreparable harm. The ISO standards are the result of great effort by a committee of health and safety management experts who worked closely at a number of other approaches to system management — including ISO 9001 and ISO 14001. In addition, ISO 45001 was designed to take other existing occupational health and safety standards, such as OHSAS 18001, into account — as well as the ILO’s labor standards, conventions and safety guidelines.
According to health and safety expertise of [Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK] — including the professionals who worked on the ISO committee — ISO 45001 represents a very good standard taking care of OH&S Hazards and Risks and opportunities. Businesses of all sizes and nature, Government or non-Government, Private or public, Large of SMEs can now access a single framework that offers them a clear pathway to developing better and more robust occupational health and safety measures.
Especially geared toward senior management and their accountabilities, ISO 45001 has the ultimate goal of helping businesses provide a healthy and safe working environment for their employees and everyone else who might visit the workplace. This goal can be achieved by controlling factors that could potentially lead to injury, illness and — in extreme situations — even death. As a result, ISO 45001 is concerned with mitigating any factors that are harmful or that pose a danger to workers’ physical and/or mental well-being.
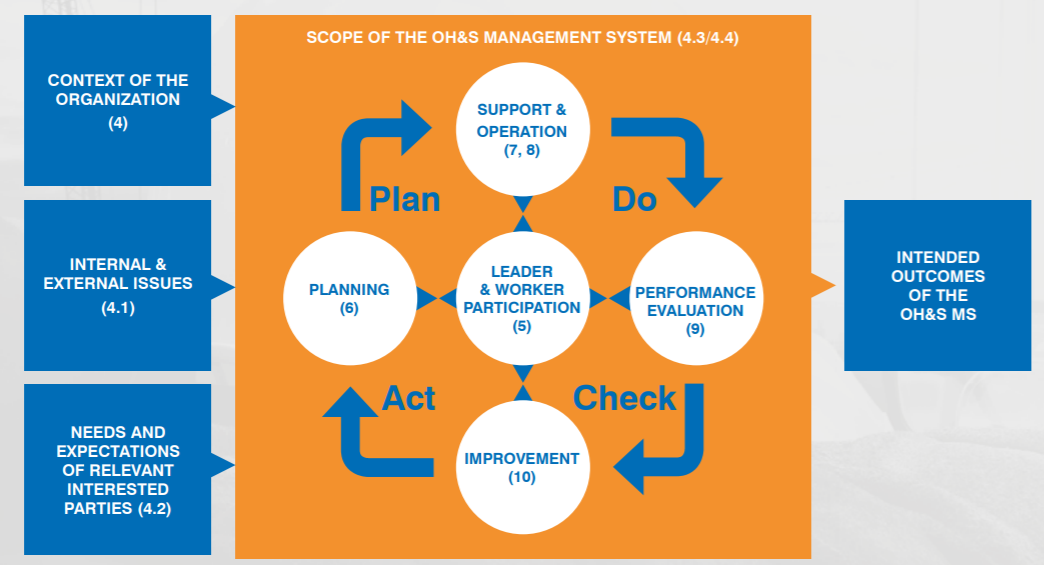
Although ISO 45001 is a transition from OHSAS 18001:2007, it’s a distinctly new standard — not a simple revision or brief update. The ISO 45001:2018 standard structure is the same as ISO High Level Structure or Annex SL.

ISO 45001:2018 uses PDCA Cycle:
Who are the intended users of the Standard?
All organizations large, corporate or SME, Government, or non-Governmental, Private or Public- irrespective of size, nature of business, locations and complexities can implement ISO 45001:2018 and get certified to it from Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK, as long as the organisation has people working, or who may be affected by its activities, then using a systematic approach to managing OH&S will bring benefits to it. The standard can be used by small low-risk operations equally as well as by high risk and large complex organisations. While the standard requires that OH&S hazards and risks and opportunities are addressed and controlled, it also takes a risk-based approach to the OH&S management system itself, to ensure
a) that it is effective and
b) being improved to meet an organization’s ever changing “context”.
This risk-based approach is consistent with the way organisations manage their other “business” risks and hence encourages the integration of the standard’s requirements into organizations’ overall management processes.
How does ISO 45001 relate to other standards?
ISO 45001 follows the high-level structure approach- Annex SL (renamed as Annex L) that is being applied to various other ISO management system standards, such as ISO 9001:2015 (quality) and ISO 14001:2015 (environment). In developing the standard, ISO has given consideration to the content of other international standards (such as OHSAS 18001 or the International Labour Organisation’s “ILO –OSH Guidelines”) and national standards, as well as to the ILO’s International Labour standards and conventions (ILSs).
Those adopting the standard, and getting certified from Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK should find its requirements consistent with the other standards. This will allow for a relatively easy migration from using an existing OH&S management system standard to using ISO 45001:2018, and will also allow for the alignment and integration with the requirements of other ISO management system standards into their organization’s overall management processes.
What will be the benefits of using ISO 45001 and Certification from Euro Veritas (BAR Accreditated)?
An ISO 45001 based OH&S management system and certification from Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK will enable the said organisation to improve its OH&S performance by:
• Developing and implementing an OH&S policy and OH&S objectives
• Establishing systematic processes which consider its “context” and which take into account its risks and opportunities, and its legal and other requirements
• Determining the hazards and OH&S risks associated with its activities; seeking to eliminate them, or putting in controls to minimize their potential effects
• Establishing operational controls to manage its OH&S risks and its legal and other requirements
• Increasing awareness of its OH&S risks
• Evaluating its OH&S performance and seeking to improve it, through taking appropriate actions
• Ensuring workers take an active role in OH&S matters
Henceforth, these measures will ensure that an organization’s reputation as a safe place to work will be promoted, and can have more direct benefits, such as:
• Improving its ability to respond to regulatory compliance issues
• Reducing the overall costs of incidents
• Reducing downtime and the costs of disruption to operations
• Reducing the cost of insurance premiums
• Reducing absenteeism and employee turnover rates
• Recognition for having achieved an international benchmark (which may in turn influence customers who are concerned about their social responsibilities)

Is ISO 45001 certification right for me?
If you have certification to OHSAS 18001 from Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK you will need to do a transition to ISO 45001:2018 before March 2021 to maintain the validity of certification.
ISO 45001 is right if you and your organization need to demonstrate a commitment in managing the safety of workers and interested parties. If you have already implemented a quality or environmental management system aligned with the new Annex SL structure ISO 45001 can be integrated smoothly. Organizations that implement ISO 45001 need:
• a clear management structure with defined authority and responsibility
• defined objectives for improvement, with measurable results
• a structured approach to risk assessment and reduction
Health & safety management failures, performance and the review of policies and objectives should be regularly monitored to ensure improvements and business benefits are realized and prioritized accordingly.
Some ILO understandings:
Guidelines on occupational safety and health management systems -ILO-OSH 2001 (Relevant ILO Conventions and Recommendations)
Conventions
No. Title
115 Radiation Protection, 1960
135 Workers’ Representatives, 1971
136 Benzene, 1971
139 Occupational Cancer, 1974
148 Working Environment (Air Pollution, Noise and Vibration), 1977
155 Occupational Safety and Health, 1981
161 Occupational Health Services, 1985
162 Asbestos, 1986
167 Safety and Health in Construction, 1988
170 Chemicals, 1990
174 Prevention of Major Industrial Accidents, 1993
176 Safety and Health in Mines, 1995
*184 Safety and Health in Agriculture, 2001
*187 Promotional Framework for Occupational Safety and Health, 2006
*P155 Protocol of 2002 to the Occupational Safety and Health Convention, 1981
Recommendations
No. Title
114 Radiation Protection, 1960
144 Benzene, 1971
147 Occupational Cancer, 1974
156 Working Environment (Air Pollution, Noise and Vibration), 1977
164 Occupational Safety and Health, 1981
171 Occupational Health Services, 1985
172 Asbestos, 1986
Documentation Required in ISO 45001:2018:
ISO 45001:2018 standard essentially allows the organization to tailor and customize the completeness or complexity of documentation to its own situation, as long as it still achieves its overall objectives. This approach does not, however, lessen the requirement for proper documentation. As noted in the standard, “documented information” is a requirement:
• When information needs to be disseminated or shared.
• To prove and retain that proof, that a process has been completed and if intended results were achieved.
• To retain knowledge relevant to the organization, including:
• QH&S MS Manual & Procedures, Instructions
• Hazard/Risk Assessment Matrix
• Processes
• Specifications/Revisions
• Goals/Expectations
• Monitoring/Measurements
• Analysis/Reviews/Evaluations /Validations
• Terminology
• Decisions Made
• Negotiations
• Notifications
• Authorizations
• Actions taken
• Assets/Inventories/Property Management
• Position Descriptions/Qualifications
• Etc
Guidelines on what to document can include: Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK generally looks out for the following:
• Documenting critical requirements of the OH&S management system, such as its scope, key operational processes, policies, and objectives
• Documenting the OH&S MS Manual, Procedures, Operational Controls, Instructions
• Documenting the Hazard Identification / Risk Assessment Matrix
• Documenting important, but perhaps less critical information that supports the OH&S such as process flow charts, specific health and safety and operational procedures, schedules, information collection approaches, such as record keeping forms, surveys) business plans, etc.
Required Documented Information
4.3 - The scope of OH&S and the Organization to be available as documented information
5.2 - The OH&S policy (approved from Top Management) available as documented information
5.3 - The responsibilities, accountabilities, and authorities for relevant roles/positions are maintained as documented information
6.1.1 - Maintain documented information of the OH&S risks and OH&S opportunities and the processes needed to address risks and opportunities
6.1.2.2 - The methodologies and criteria for assessing OH&S risks are defined, maintained and retained as documented information
6.1.3 - Information on applicable legal and other requirements are maintained, retained, and updated as documented information
6.2.2 - The OH&S objectives and plans to achieve them are maintained and retained as documented information
7.2 - Documented information is retained as evidence of competence of workers
7.4 - Relevant OH&S communications are received and maintained as documented information
8.1.1 - Documented information to provide confidence that processes have been carried out as planned and determining where the absence of documented information could lead to deviations from the OH&S policy and the OH&S objectives is kept
8.6 - Information on the process and on the plans for responding to potential emergency situations are maintained and retained as documented information
9.1.1 - Evidence of the monitoring, measurement, analysis and evaluation results are retained as documented information
9.1.2 - Results of the compliance evaluation are retained as documented information
9.2.2 - Evidence of the implementation of the audit program and the audit results is retained as documented information
9.3 - Evidence of the results of management reviews is retained as documented information
10.1 - Evidence of the nature of incidents or nonconformities and actions taken with results and effectiveness of correction is retained as documented information and communicated to relevant workers other relevant interested parties
10.2.2 - Evidence of the results of continual improvement efforts is retained as documented information
Example of some Operational Controls which might be relevant to your workplace- which have to be documented and implemented are:
• Electrical safety
• Fire safety
• Gas safety
• Harmful substances
• Machinery, plant and equipment
• Manual handling
• Noise
• Personal protective equipment
• Pressure equipment
• Radiations
• Slips and trips
• Vibration
• Working at height
• Working in confined spaces
• Workplace transport
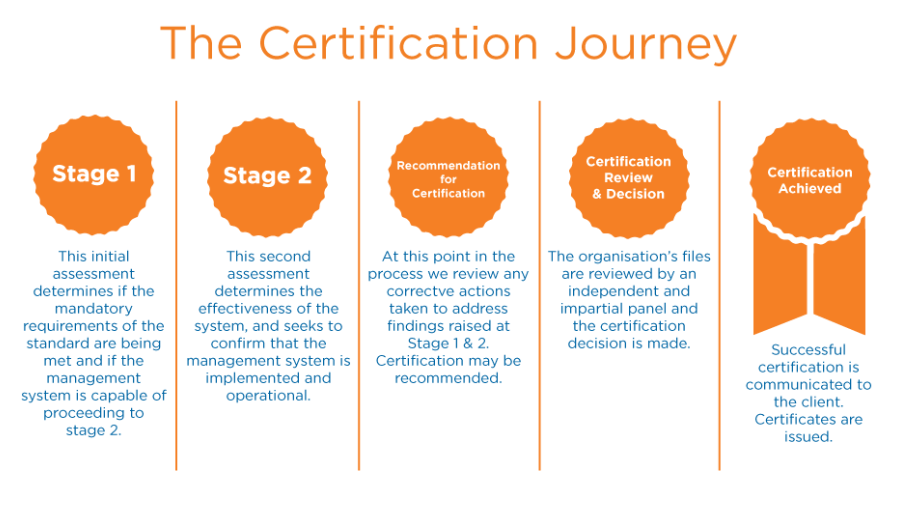
The Certification Journey with Euro Veritas, UK (www.euroveritas.com) accreditated from BAR-UK: